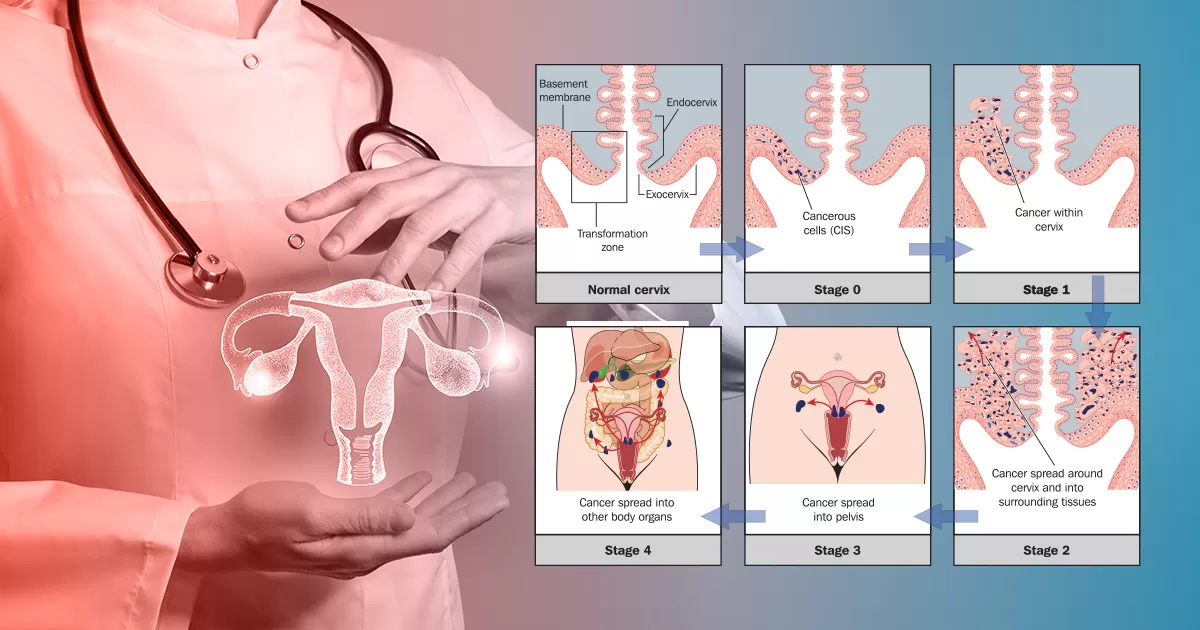
Cervical cancer, a significant health concern for women worldwide, progresses through distinct stages that necessitate careful understanding for effective treatment planning. Understanding these stages is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers to plan the most effective course of action. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore each stage, shedding light on the characteristics, diagnostic methods, and potential treatment options.
Stage 0: Carcinoma in Situ
In the initial stage, known as Carcinoma in Situ (CIS), abnormal cells are detected on the cervix surface. This pre-cancerous stage is often identified through routine screenings like Pap smears and HPV tests. Treatment options at this point include cryotherapy and laser therapy, non-invasive procedures that aim to eliminate abnormal cells.
Stage I: Early Localized Cancer
Stage IA
At Stage IA1, the tumor is microscopic with a depth of invasion less than 3mm. Treatment often involves procedures like cone biopsy or loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP). In Stage IA2, the microscopic tumor has a depth of invasion between 3mm and 5mm, with similar treatment approaches.
Stage IB
Stage IB1 signifies a visible lesion of 4cm or smaller on the cervix, and treatments may include radical hysterectomy or trachelectomy. In Stage IB2, where the lesion is larger (more than 4cm but not exceeding 5cm), a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and possibly chemotherapy may be recommended.
Stage II: Cervical Cancer Extending Beyond the Uterus
Stage IIA
In Stage IIA1, the tumor involves the upper two-thirds of the vagina, measuring 4cm or smaller. Treatments may include surgery, radiation therapy, or a combination. Stage IIA2, with a larger tumor exceeding 4cm, might require more extensive surgery along with radiation therapy and possibly chemotherapy.
Stage IIB
Stage IIB indicates the invasion of the tumor into tissues next to the uterus but not the pelvic sidewall. Treatment often involves a combination of external beam radiation therapy, brachytherapy, and, in some cases, chemotherapy. Surgery may also be considered in conjunction with radiation.
Stage III: Cancer Spreading Locally
Stage IIIA
Cancer spreading to the lower third of the vagina characterizes Stage IIIA. Treatment options include radical hysterectomy or a combination of radiation therapies.
Stage IIIB
If cancer invades the pelvic sidewall or causes hydronephrosis, a more aggressive approach is needed. Chemoradiation or pelvic exenteration (surgical removal of affected tissues) may be considered.
Stage IIIC
At Stage IIIC, cancer has spread to pelvic or para-aortic lymph nodes. A combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy is typically recommended. Palliative care may be introduced if a cure is challenging.
Stage IV: Advanced Cancer
Stage IVA
Stage IVA indicates the spread of cancer to adjacent organs like the bladder or rectum. Palliative care becomes crucial for symptom management, and various combination therapies are employed to slow down disease progression.
Stage IVB
In the advanced Stage IVB, cancer has spread to distant organs such as the lungs, liver, or bones. Palliative care is central to managing symptoms, and chemotherapy and targeted therapies may be used to control cancer spread and enhance overall well-being.
Importance of Regular Screenings
Regular screenings, such as Pap smears and HPV tests, serve as indispensable tools in the early detection of cervical abnormalities. These screenings can identify precancerous changes long before they develop into invasive cancer, enabling timely intervention and improving the chances of successful treatment.
By undergoing routine screenings as part of preventive healthcare, women empower themselves with knowledge about their cervical health. Early detection not only allows for more effective treatment options but also reduces the emotional and physical toll associated with advanced stages of the disease. Regular screenings are, therefore, a cornerstone in the proactive management of cervical cancer.
The Role of Vaccinations
Vaccinations, specifically against the human papillomavirus (HPV), play a pivotal role in preventing cervical cancer. HPV is a common virus that can lead to cervical cancer and other related cancers. Vaccinating individuals before exposure to the virus provides powerful protection against HPV-related diseases.
The HPV vaccine is a crucial component of preventive healthcare for both adolescents and young adults. By getting vaccinated, individuals not only protect themselves but also contribute to the broader effort of creating herd immunity. This collective protection is instrumental in reducing the overall prevalence of HPV and, consequently, the incidence of cervical cancer.
In addition to regular screenings, vaccinations contribute to a comprehensive strategy for cervical cancer prevention. As we navigate the stages of this disease, the importance of these preventive measures cannot be overstated. They not only save lives but also embody a commitment to the well-being of individuals and communities.
The journey through the stages of cervical cancer is inherently intertwined with the proactive steps we take for prevention. Regular screenings and vaccinations emerge as powerful tools, offering a shield against the impact of this disease. As we navigate these complexities, let us advocate for and embrace these preventive measures, ensuring that women have the knowledge and resources needed to prioritize their cervical health.
Understanding the nuances of each stage is vital for both patients and healthcare providers. It not only guides treatment decisions but also empowers individuals to navigate the complexities of cervical cancer with resilience and hope. Regular communication with healthcare teams and access to supportive services remain crucial throughout the journey.
Shinon Healthcare is dedicated to spreading awareness about cervical cancer and promoting women’s health. By providing valuable resources, education, and support, Shinon Healthcare contributes to the holistic well-being of women facing the challenges of cervical cancer. Through our dedication to expanding medical knowledge and engaging with communities, Shinon Healthcare humbly strives to emphasize the significance of collaborative efforts in improving women’s health globally.